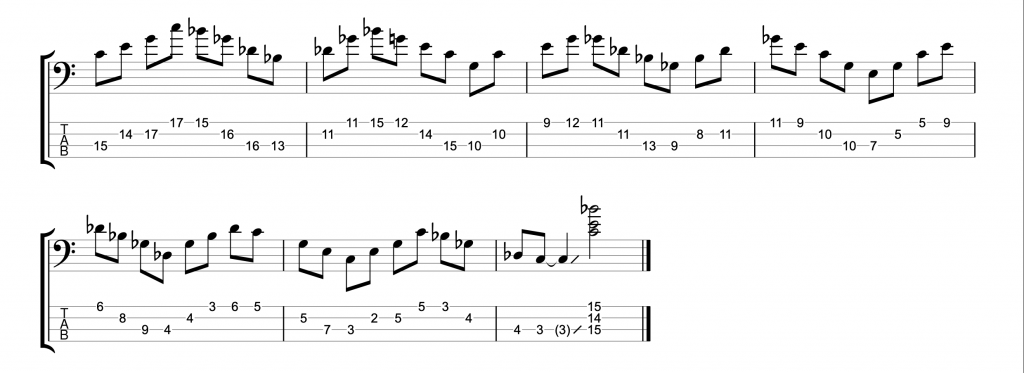
Jazz Solo Lines for 4-String Bass with Bass Tab – Bass Practice Diary – 27 April 2021
This week I’m featuring three jazz solo lines that I’ve adapted to be played on 4-string bass. I’ve been thinking recently about how I first learned jazz on bass as a teenager. I started out with a 4-string bass, like most bass players do. In recent years, I’ve done most of my jazz playing on 6-string basses. But jazz improvisation isn’t only for bass players who play extended range basses.
I didn’t play a 6-string bass until I was 19 years old. By that time, I had already completed a year of a bachelors degree at a music college. I was studying and performing music by Charlie Parker, John Coltrane, Chick Corea and others. To cut a long story short, I learned to play jazz on a 4-string bass with 20 frets. And this week I’m returning to my roots by arranging some brilliant jazz solo lines on 4-string bass.
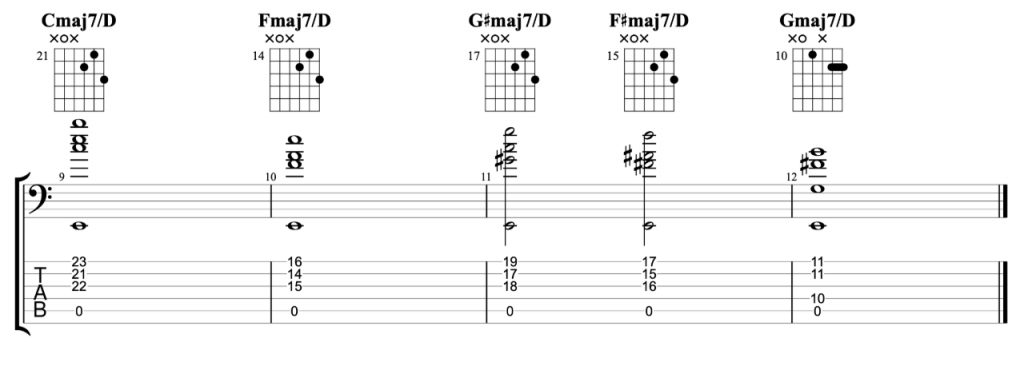
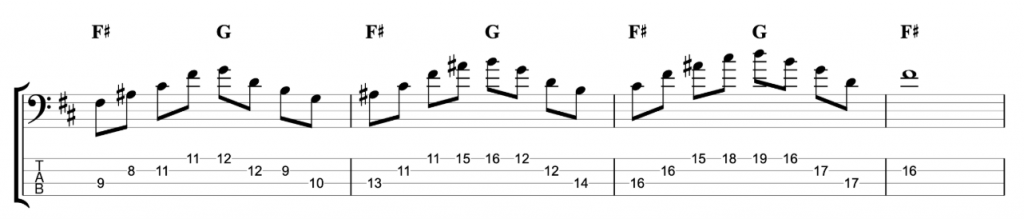
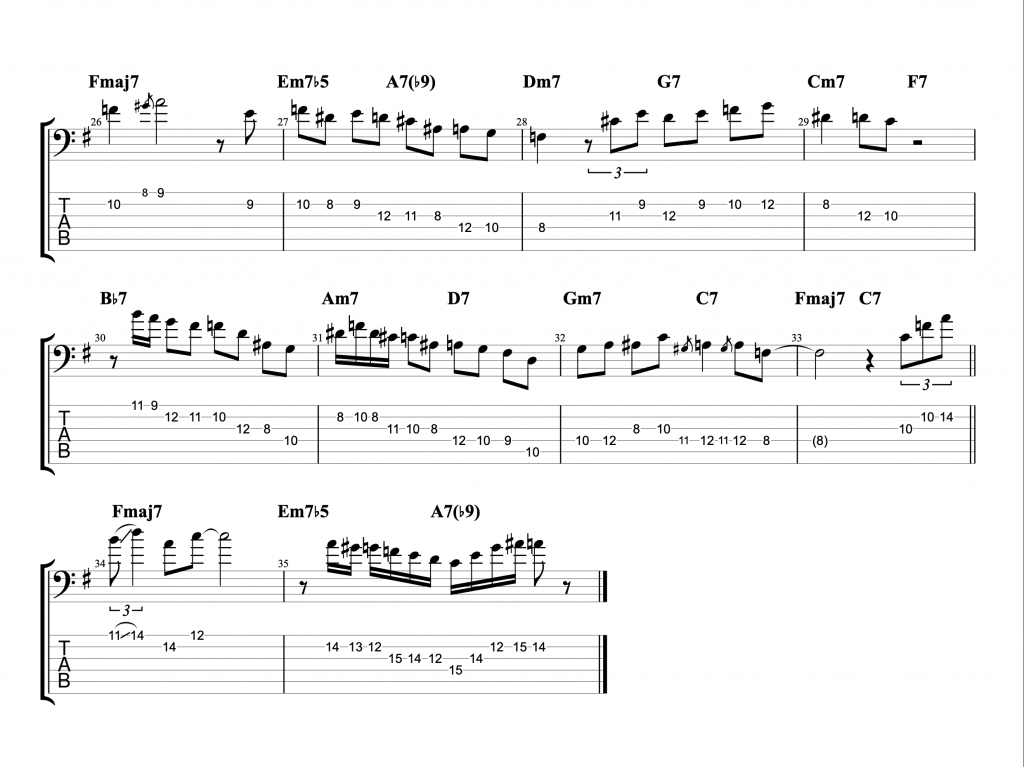
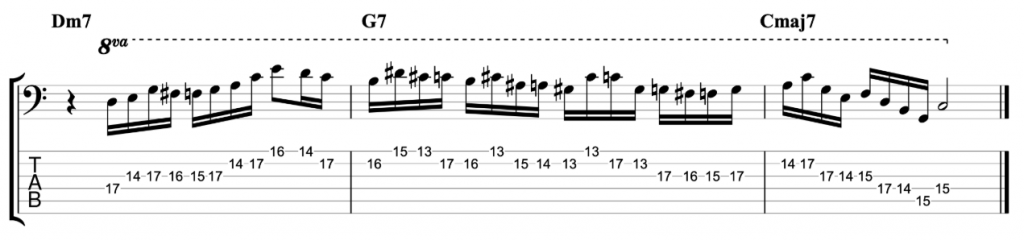
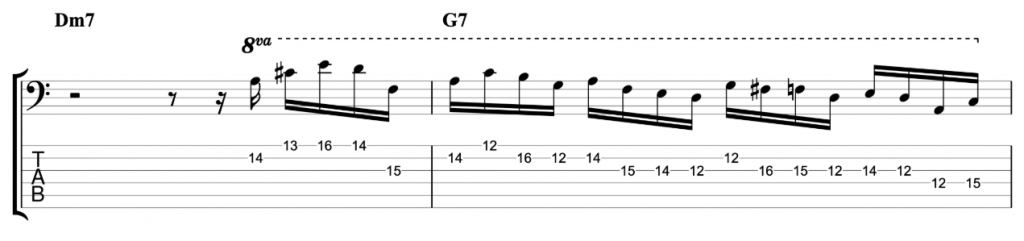
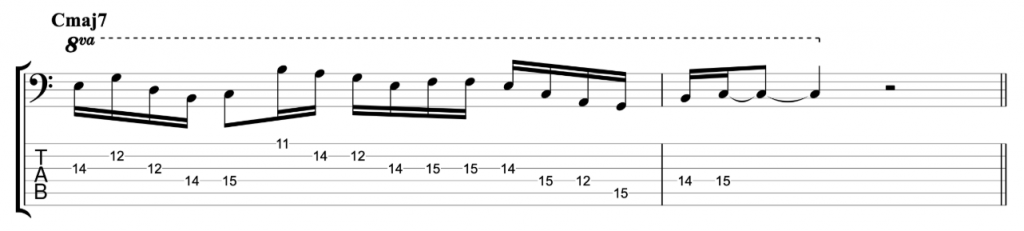
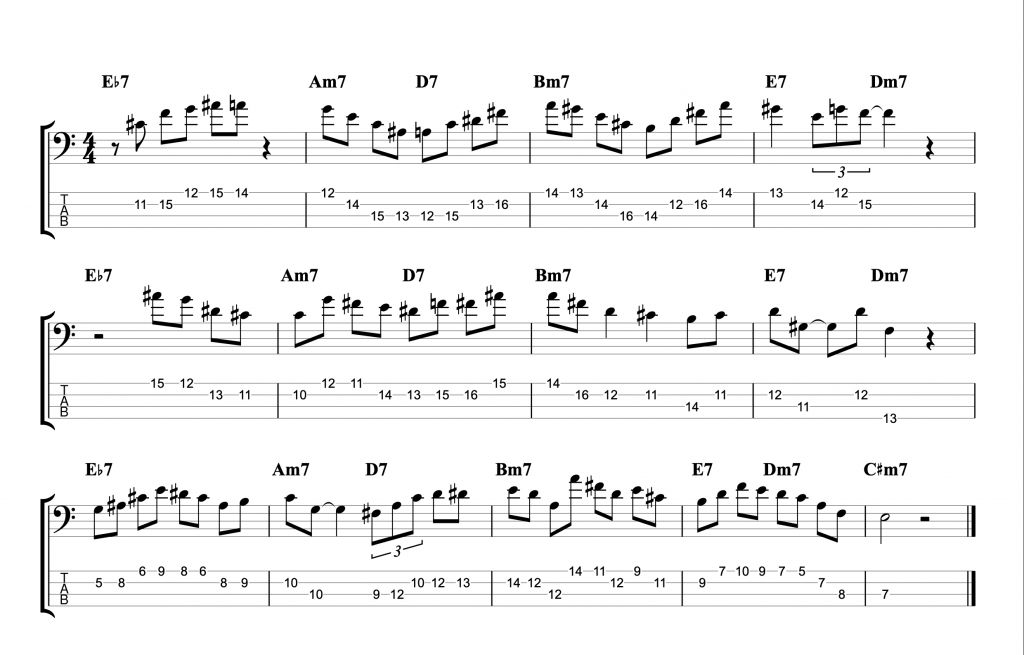
Jazz Line #1: Autumn Leaves, Keith Jarrett

This line comes from Keith Jarrett’s brilliant trio album Still Live with Gary Peacock and Jack DeJohnette. It’s played in the last eight bars of the first chorus of the piano solo on the classic jazz standard Autumn Leaves. He doesn’t play any left hand chord voicings during the line. So, the chord symbols written above represent the implied harmony and you shouldn’t necessarily take them too literally. One of the great things about that ‘standards trio’ was the way they interpreted the harmony of standards so loosely and with such freedom. This line is just a great example of a jazz solo line improvised by a wonderful musician on a classic standard.
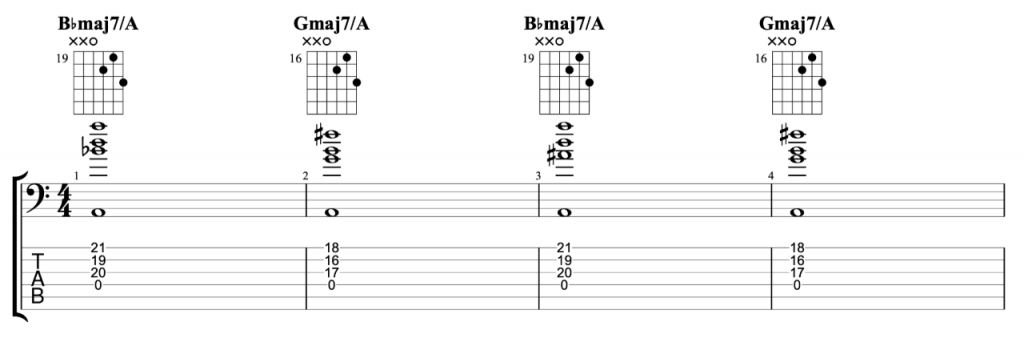
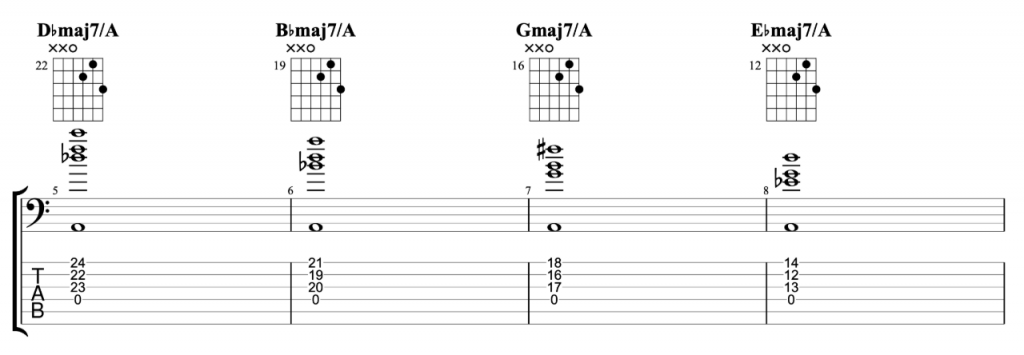
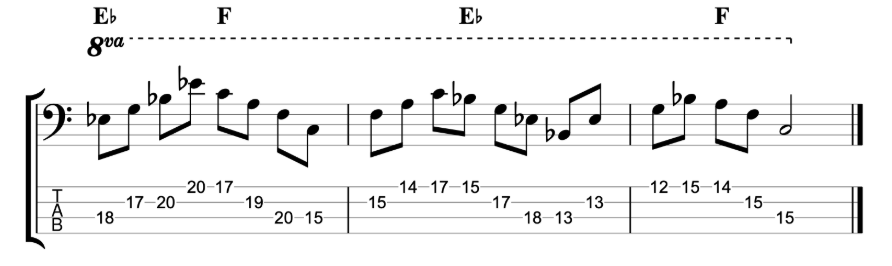
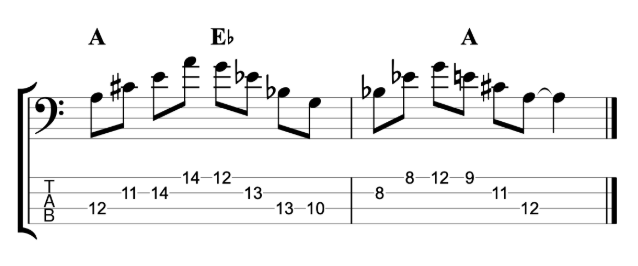
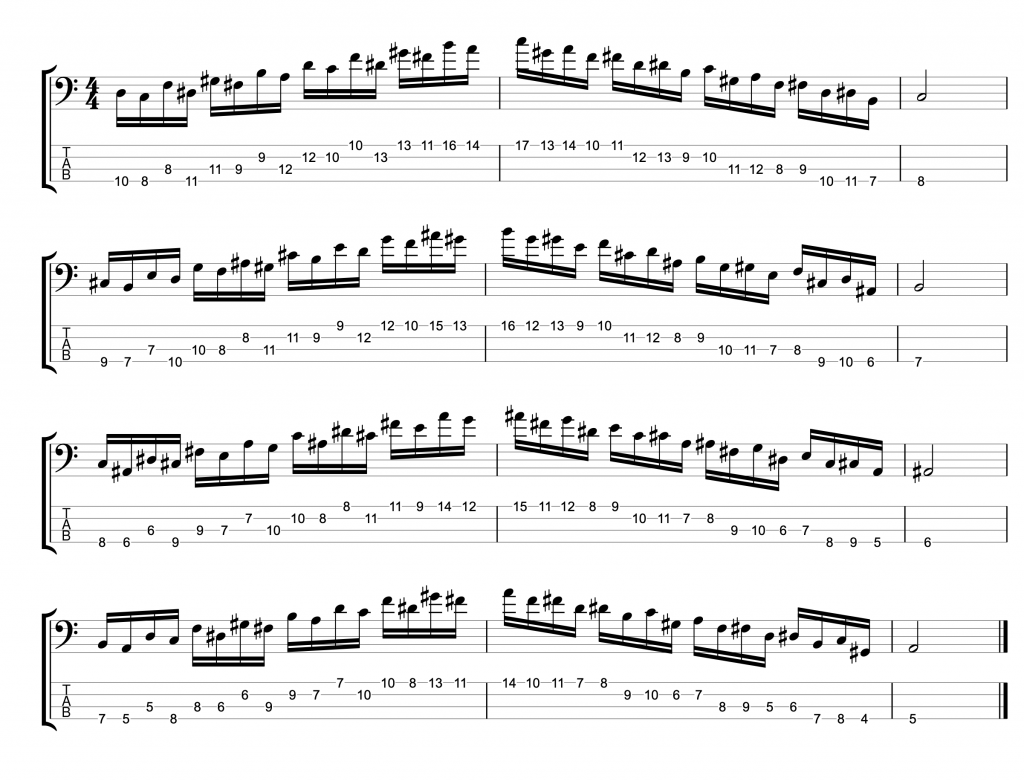
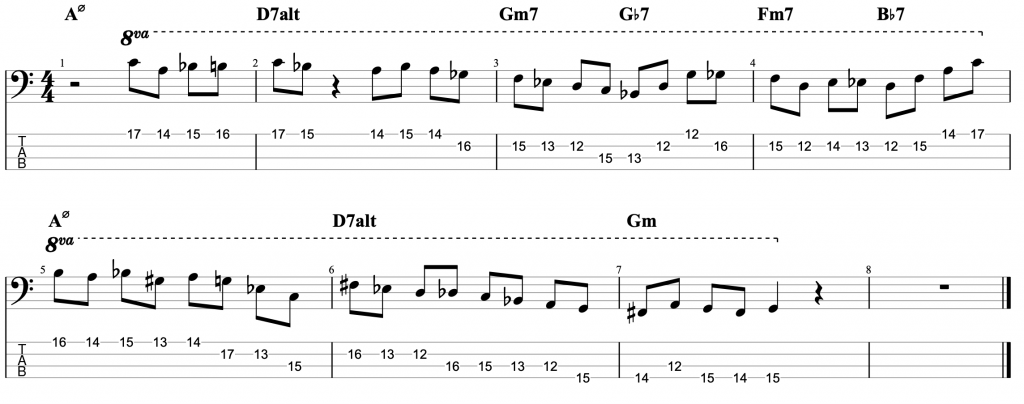
Jazz Line #2: Whole-tone Line in Cm, Mike Stern
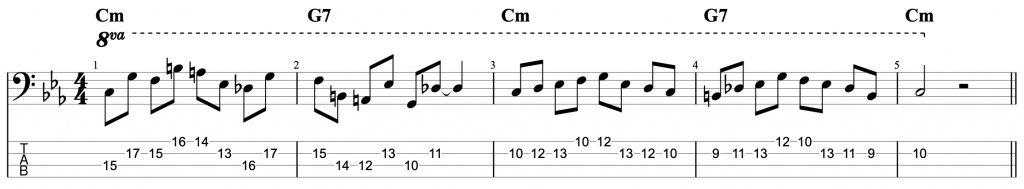
This second line doesn’t come from a recording, but from a book. It’s a brilliant book by the legendary guitarist Mike Stern called Altered Scale Soloing for Jazz Guitar. It comes in a chapter where he’s talking about using the whole-tone scale to create an altered dominant sound. The chord progression in the example is simply I-V in C minor. If you play a whole-tone scale over the dominant V chord, it gives you the root, 9th, 3rd, #11, b13 and dominant 7th. It’s an interesting mix of chord tones and alterations. And this line is a great example of how to create a modern sounding altered jazz line in a minor key.
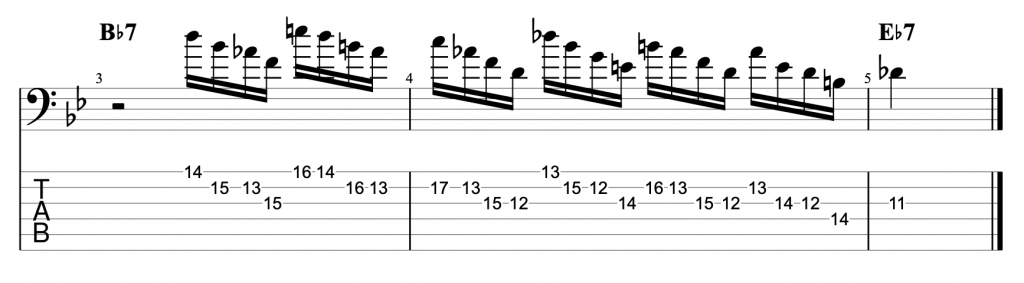
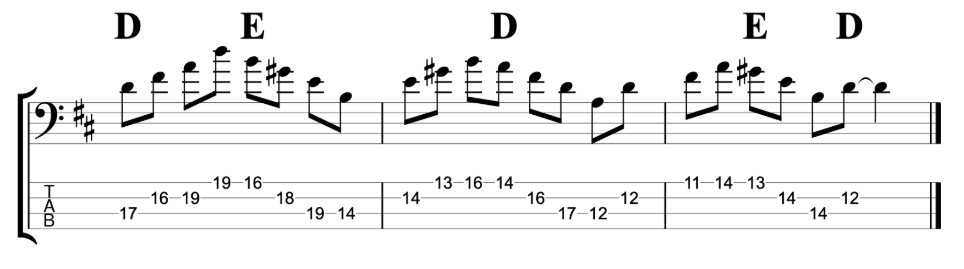
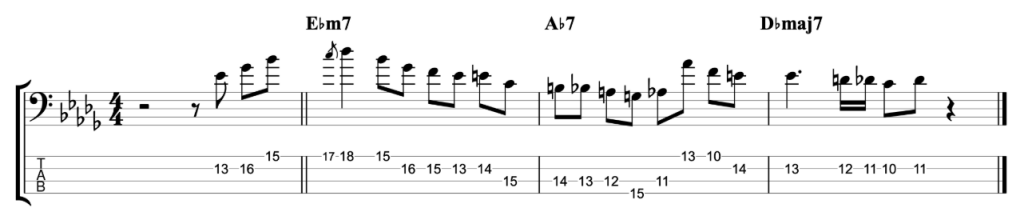
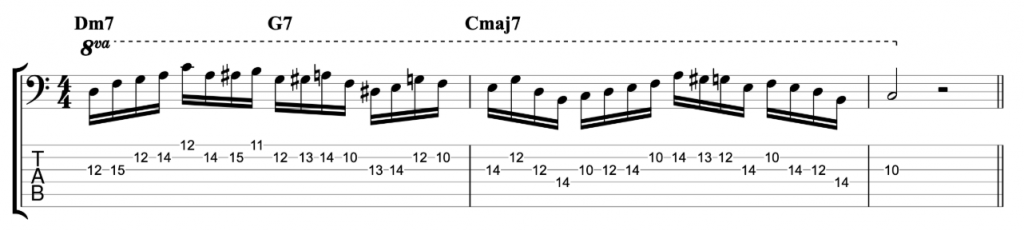
Jazz Line #3: Oleo (Bb Rhythm Changes), Niels Henning Orsted Pedersen
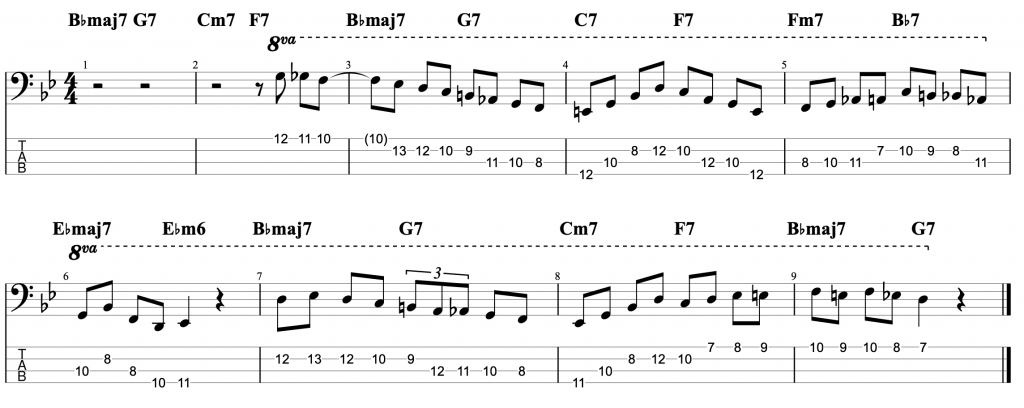

The third and final line comes from the brilliant duet album Chops by Joe Pass and the incredible double bassist Niels-Henning Ørsted Pedersen. This line is played at the start of the bass solo on Sonny Rollins’ tune Oleo. So this is a line that you can use on any Bb ‘Rhythm Changes’ tune. Rhythm Changes is played in eight bar sections and this is played over the first A section. Although it does drift into the start of bar 9 which is the start of the second A section.
I think this line is an example of a bass player proving that the bass can be a dynamic jazz soloing instrument. Just like any other melodic or harmonic instrument. I haven’t attempted to figure out where he was playing the notes on the fretboard. My fingerings are based on how I would play this line as an electric bass player, not on how I imagine an upright player would play it. However, unlike the previous two lines, I have played this example in the same octave that Niels-Henning Ørsted Pedersen originally played it in.
In the past I’ve done some analysis of the differences between the way double bass players and bass guitar players arrange lines on the fingerboard. You can check out the video in which I analyse a jazz line by the great bassist Tom Kennedy. He started life as a double bass player. Then he transitioned onto electric bass, taking many of the upright bass techniques and fingerings with him.