Fretless Jazz Lines – Using Open Strings for Position Shifts – Bass Practice Diary – 28th May 2019
This week I’ve been coming up with jazz lines on my fretless bass. But specifically I’ve been trying to use open strings to help me make fast accurate position shifts in these jazz lines. I’ve been inspired to try this after I transcribed a blues solo played by the phenomenal bassist Tom Kennedy in last week’s practice diary video.
I think that one of the best ways to improve as a musician is to work out passages played by great musicians. I often use transcriptions and books written by other people, which are useful tools to use. But I feel that I learn the most when I work it out for myself.
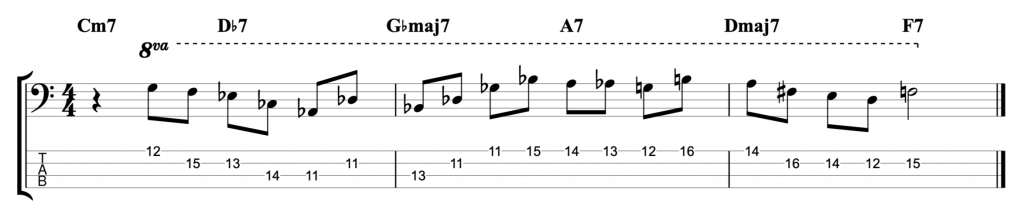
Use open strings to make position shifts
The next challenge, after you’ve worked out a piece of music, is to see what you can take from it and incorporate into your own playing. And the thing that struck me most about Tom Kennedy’s blues solo was the way he was organising his left hand and his use of the open strings.
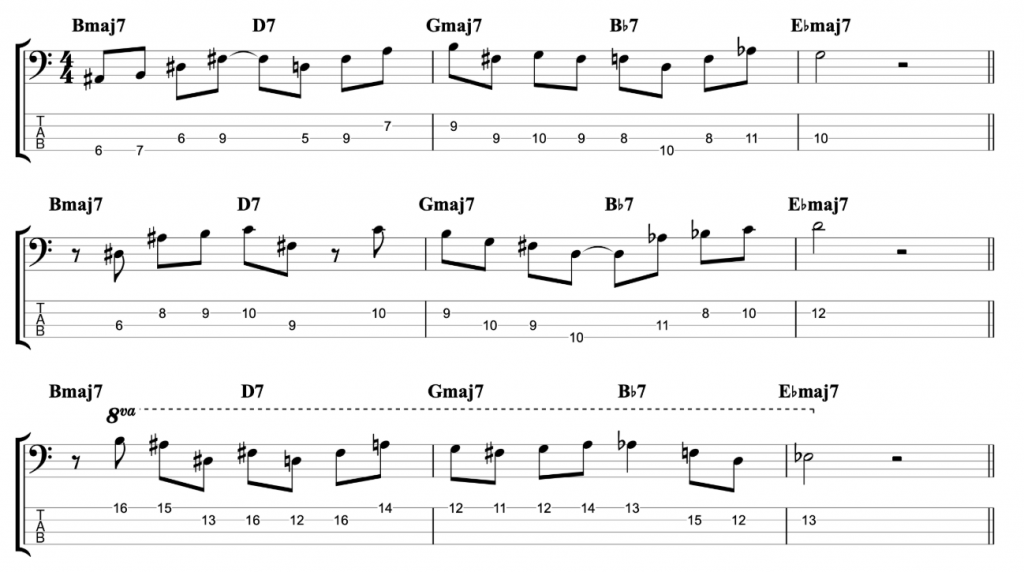
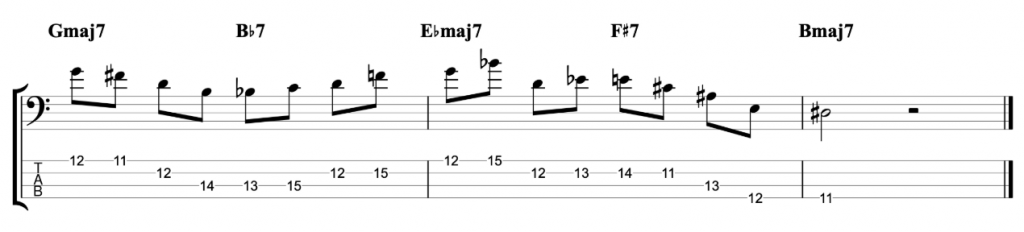
Can I take some of that and apply it to my own playing? In order to find out, I started writing out jazz lines for my fretless bass that use open strings and position shifts in the way that I’ve seen Tom Kennedy do it.
The theory behind it, is that if you play an open string before you shift position, then that gives you a little bit of extra time to make the shift. And it also gives you a reference note to help you hear if your position shift is accurately in tune. Which is extremely important on fretless bass. It’s a technique that I believe Tom Kennedy has adapted from playing upright bass. But he applies it onto fretted electric bass and he plays jazz lines at ferocious speed.
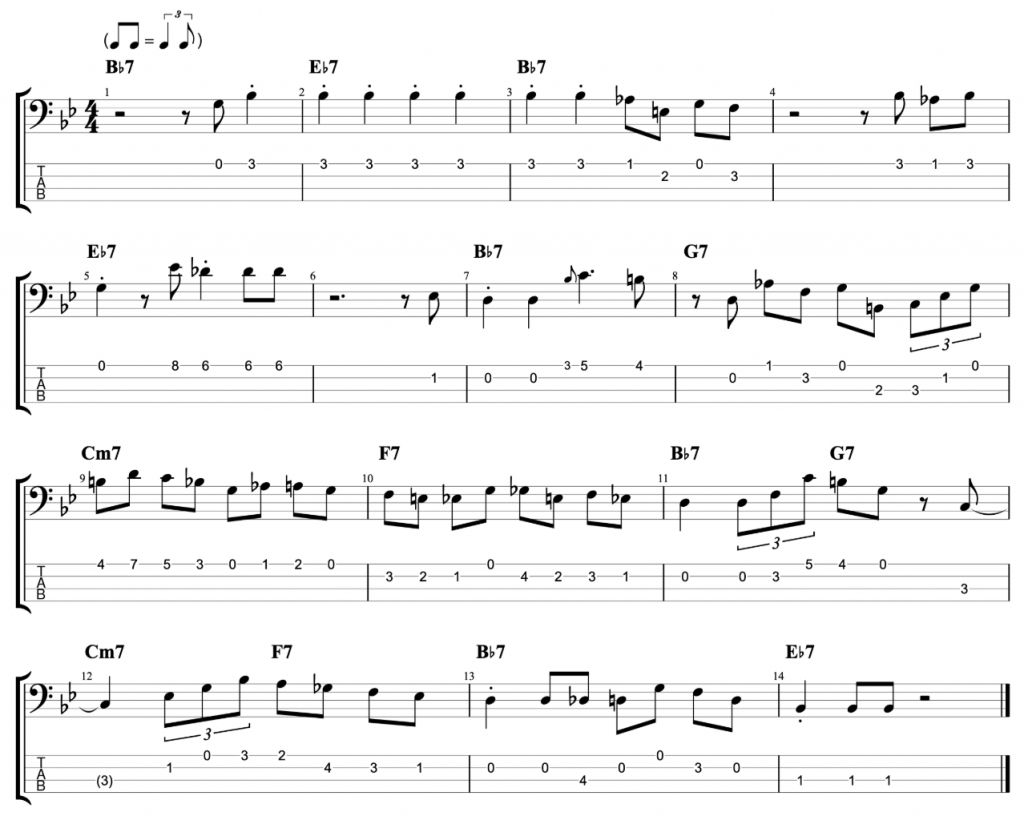
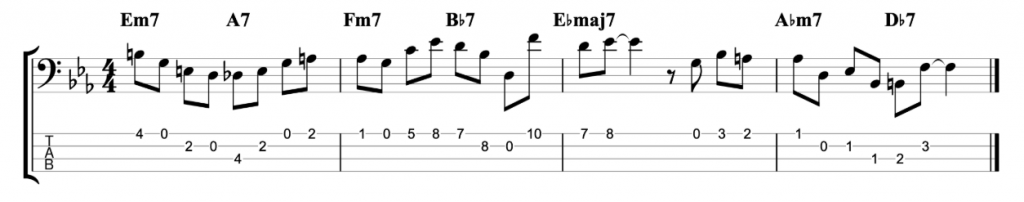
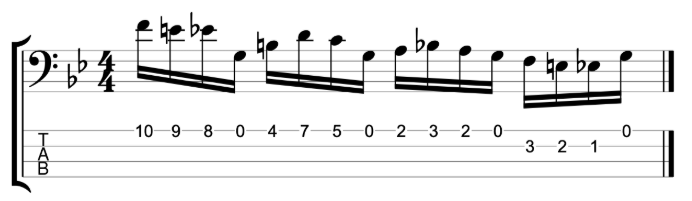
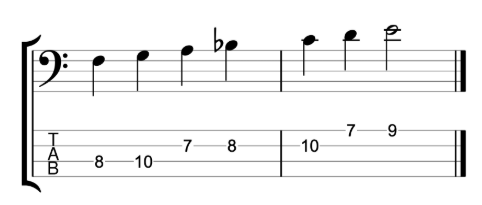
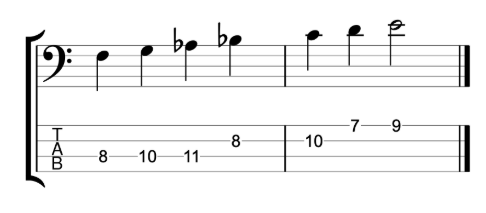
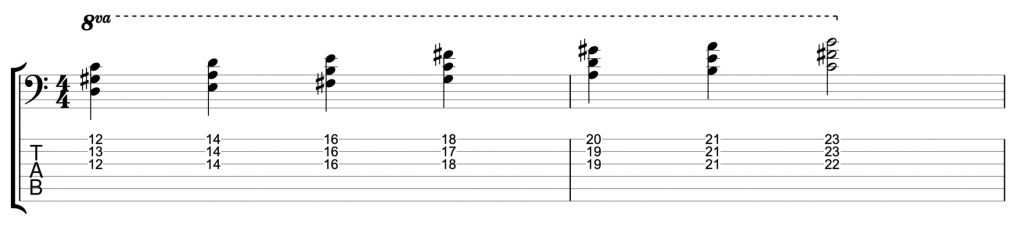
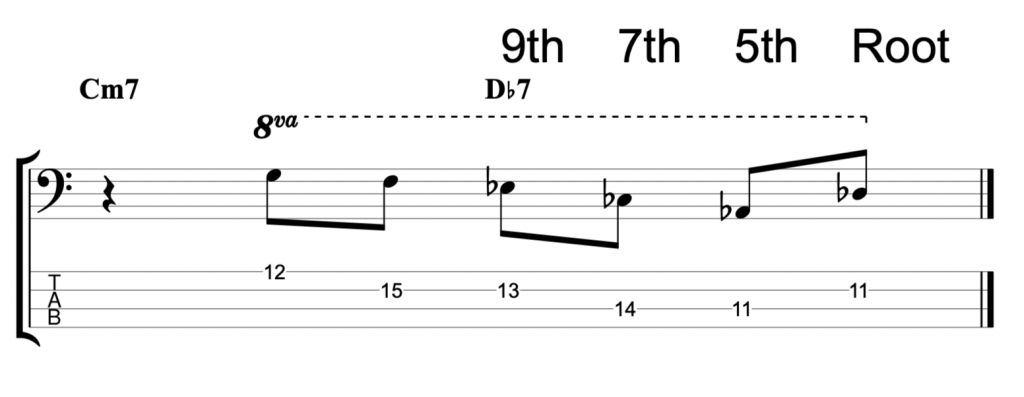
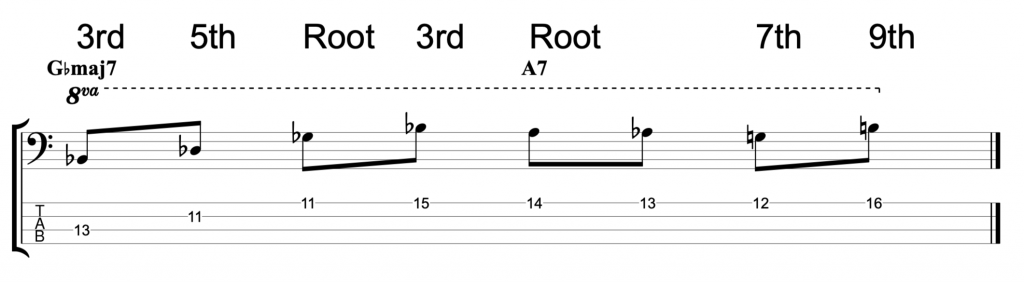
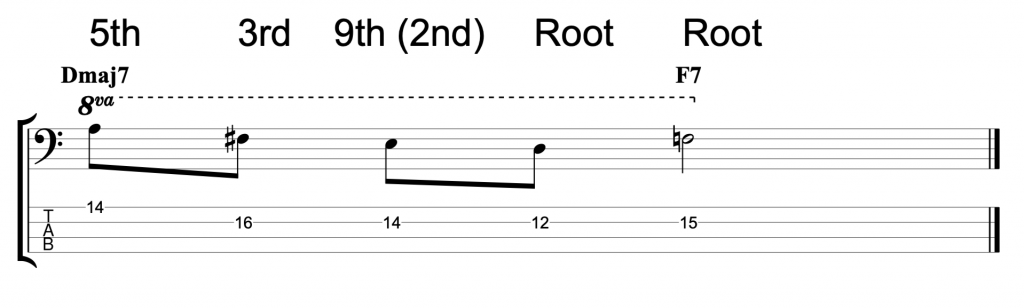
The fretless jazz lines
My fretless bass is a 6 string. I don’t have another fretless bass because I sold my four string fretless when I bought my 6 string. However, I usually write my TAB’s out for 4 string so that all bass players can use them. So, these three examples are all written for 4 string bass. Even though they’re played on 6 string in the video.
The first one that I played, at the start of the video, is written on the middle eight section of Rhythm Changes. It’s the second most popular chord progression in jazz after Blues changes.

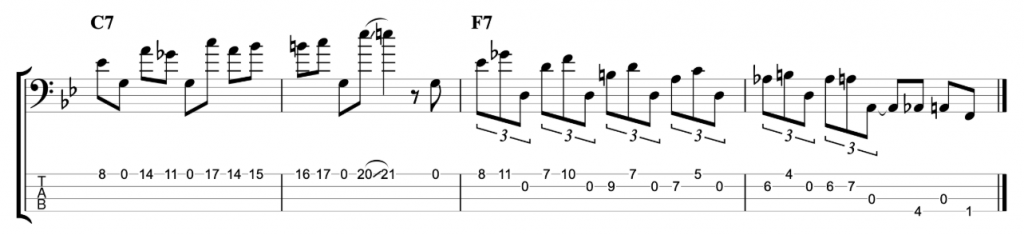
The next line that I shared in the video is meant to be played over the first four bars of Stella By Starlight.
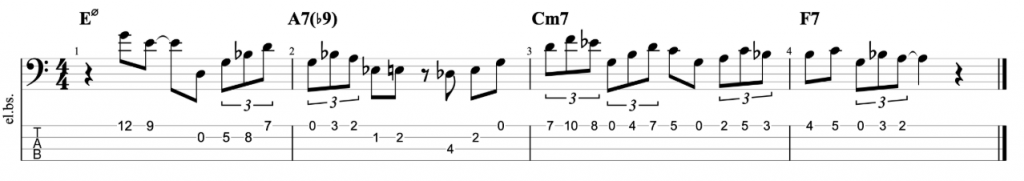
And the final example is over the changes for the first four bars of John Coltrane’s classic composition Moment’s Notice.