Minor Scales – Melodic Minor, Harmonic Minor, Natural Minor & Dorian – Bass Practice Diary – 21st January 2020
If I ask you to play a C minor scale, what do you play? Minor scales are not as simple as major scales. Most of us know what to play if someone asks us to play a C major scale, but minor scales are confusing. There are several different minor scales, and how do you know which one to play and when.
How many different minor scales are there?
If you’re going to understand minor scales, then it’s important to understand the difference between three different scales, melodic minor, harmonic minor and natural minor. Every scale is a sequence of intervals, and for each of these three scales the intervals are the same for the first five notes. It’s the 6th and 7th notes of the scales that contain the variations.
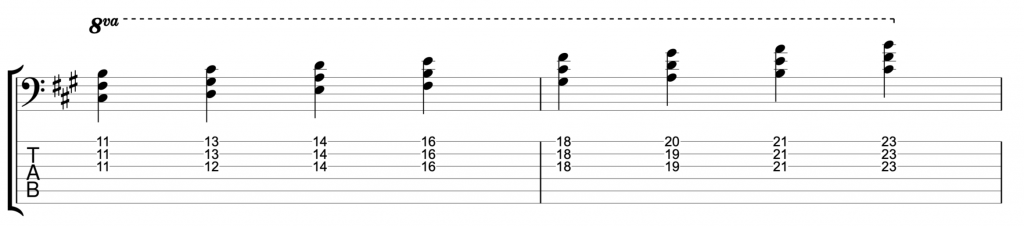
The terminology of minor scales confuses people for the simple reason that classical musicians treat minor scales differently from jazz musicians. To help explain this I’m going to start by looking at the natural minor and the melodic minor scales. I’ll use the key of A minor because it’s the simplest, it has no sharps or flats, so the natural minor scale contains the notes A, B, C, D, E, F & G.
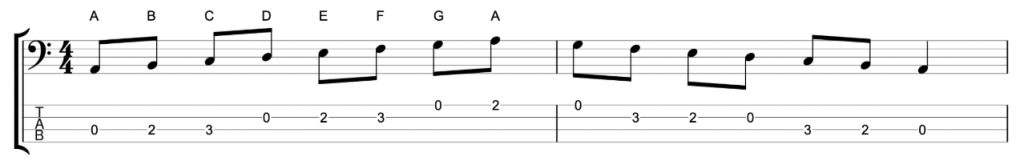
The A natural minor scale contains all of the same notes as a C major scale. That means that the natural minor scale is actually a mode of the major scale. It’s mode six, called Aeolian. Now, compare that to the melodic minor scale.
The melodic minor scale
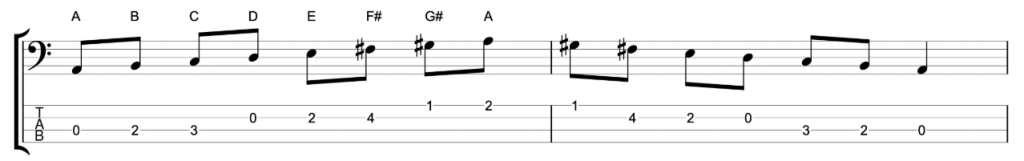
The melodic minor scale has a raised 6th and 7th, meaning F# instead of F natural and G# instead of G natural. It’s important to understand that the melodic minor scale is not a mode of the major scale like the natural minor. It’s a parent scale and has seven modes of it’s own. You can check out my video about the modes of the melodic minor scale.
So, the natural minor scale is mode six of the major scale and the melodic minor is a scale with it’s own set of modes. So, not only do these scales sound different, they are also very different in their application. The natural minor scale implies a minor 7th chord functioning as chord VI in a major key, while the melodic minor implies a minor chord with a major 7th functioning as chord I in a minor key.
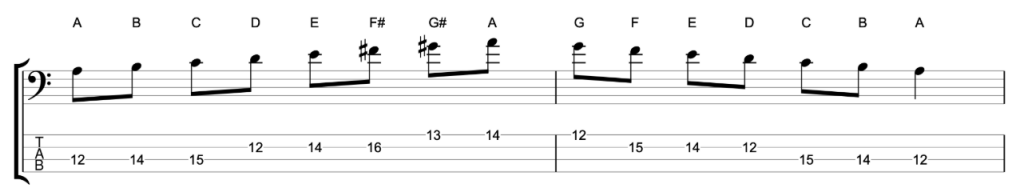
This becomes more confusing when you learn that classical music treats both these scales as one scale. The melodic minor is the ascending version of the scale, and the natural minor is the descending version of the scale. And together these are called the melodic minor. You can play it on the bass like this.
The harmonic minor scale
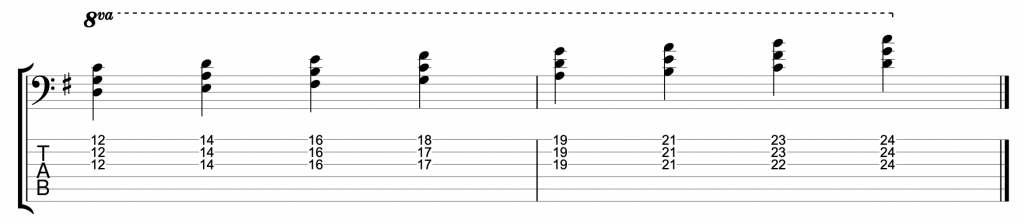
There is another minor scale, which, like the melodic minor, is a parent scale to seven of it’s own modes. It’s called the harmonic minor and it has a minor 6th and a major 7th. That means that in the key of A minor, the 6th will be an F natural and the 7th will be a G#.
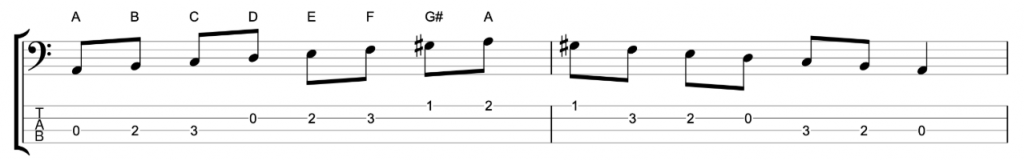
The harmonic minor scale can also imply chord I in a minor key.
The Dorian Mode
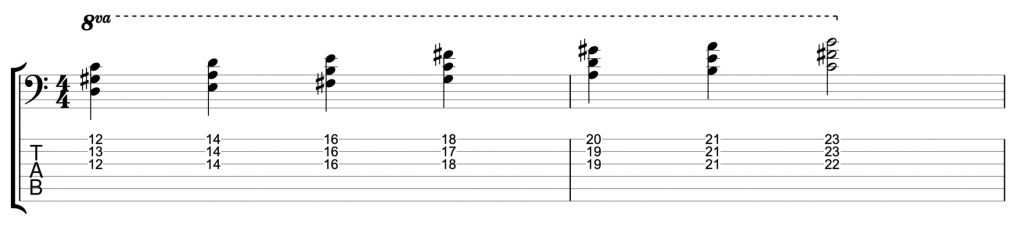
I’ve included a fourth scale in my video. The dorian scale is another mode of the major scale, mode number two. The reason I’ve included it is because it’s a much more common choice of scale for improvisers playing on minor 7th chords than the natural minor scale. However, you wouldn’t use an A dorian scale to play on chord I in the key of A minor. You would use it to play on an A minor 7th chord functioning as chord II in G major. It goes like this.

The A dorian scale contains a major 6th F# and the minor 7th G natural.