Create Chromatic Jazz Lines by Using Passing Notes – Bass Practice Diary – 19th January 2021
When you improvise a jazz line, you can put a chromatic passing note anywhere, right? That’s true up to a point. But your lines will be significantly improved if you think about where you place them. Chromatic passing notes can be used to connect scale notes and chord notes. In this video I’m looking mostly at scales, but you still need to think about where you play the chord tones. Otherwise your chromatic jazz lines can sound like you’re just playing a chromatic scale.
Chromatic Passing Notes
The idea behind chromatic passing notes is very simple. You simply move between two notes chromatically (in half steps). Major scales consist of five whole step intervals (whole tones) and two half step intervals (semitones). That means that there are five places in a major scale (or any of it’s modes) where you could place a chromatic passing note. Between any of the five whole tone intervals.
If you place a chromatic passing note in all five places, you have a chromatic scale. We don’t want our lines to sound like we’re playing a chromatic scale. We want them to sound like they belong with the harmony of the music. So, to make a chromatic jazz line sound like it fits the harmony, you need to think about what the chords are. And where are the chord tones in your line.
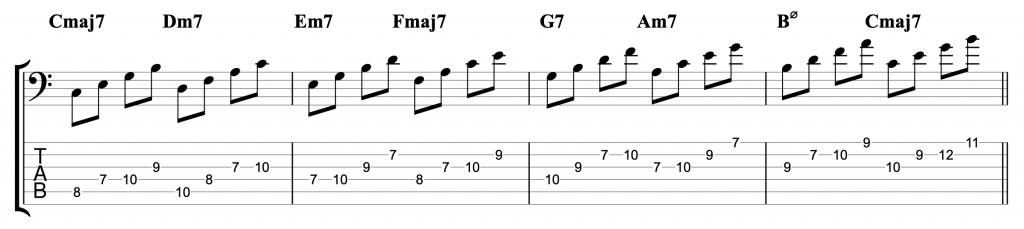
My Chromatic Jazz Line
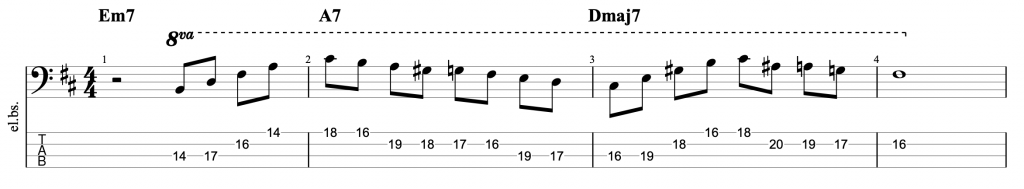
This is the line I featured in the video. I’ve used a chromatic passing note on the V chord A7. I’m thinking of the whole line as being in D major, so I’m using the notes of the D major scale. I’m also thinking about the chord tones for each chord. So, on the A7 I’m thinking about A, C#, E & G. The one chromatic passing note that I’ve included on the second bar is placed between the root note, A and the 7th, G. I’ve done that to ensure that both notes land on the beats, while the chromatic passing note (G#) lands on the off-beat.
The rest of the notes in that bar are taken from the D major scale (or A mixolydian mode). The addition of that one passing note between the root and 7th ensures that a chord note lands on every beat. The notes on the off-beats act as passing notes (either scale notes or that one chromatic note). This basically gives us what is known as a bebop scale.
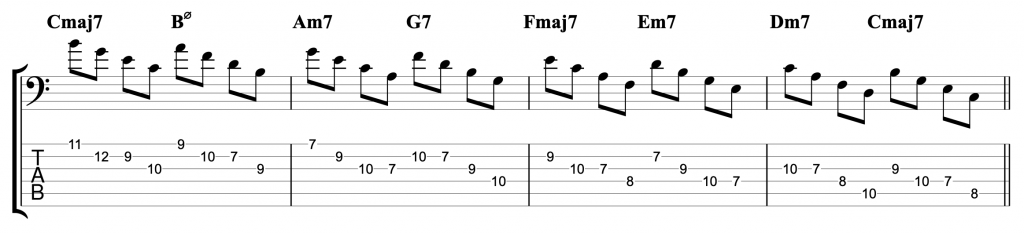
Bebop Scales and Beyond
A bebop scale on a dominant 7th chord is just the notes of the mixolydian mode with the addition of that one chromatic passing note between the root and 7th. It’s a useful scale because if you start by playing a chord tone on beat one, as I did. You can play the scale either descending or ascending. If you play 8th notes starting on beat one, you will hit a chord tone on every beat.
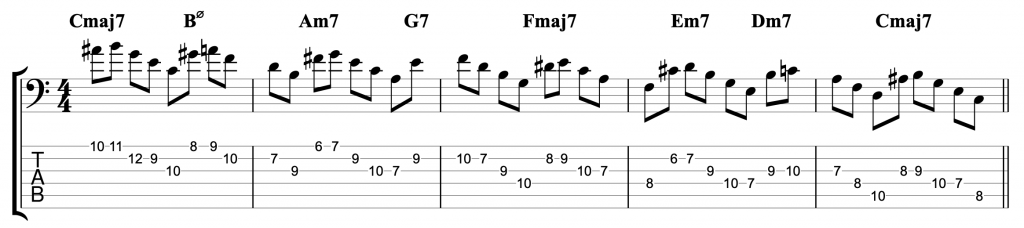
That’s not the only bebop scale. There is one for major chords as well that involves adding a chromatic passing note between the fifth and sixth notes of a major scale. There are three other bebop scales which I might cover in a future video. The dominant 7th version that I’ve used here is the one I use most often.
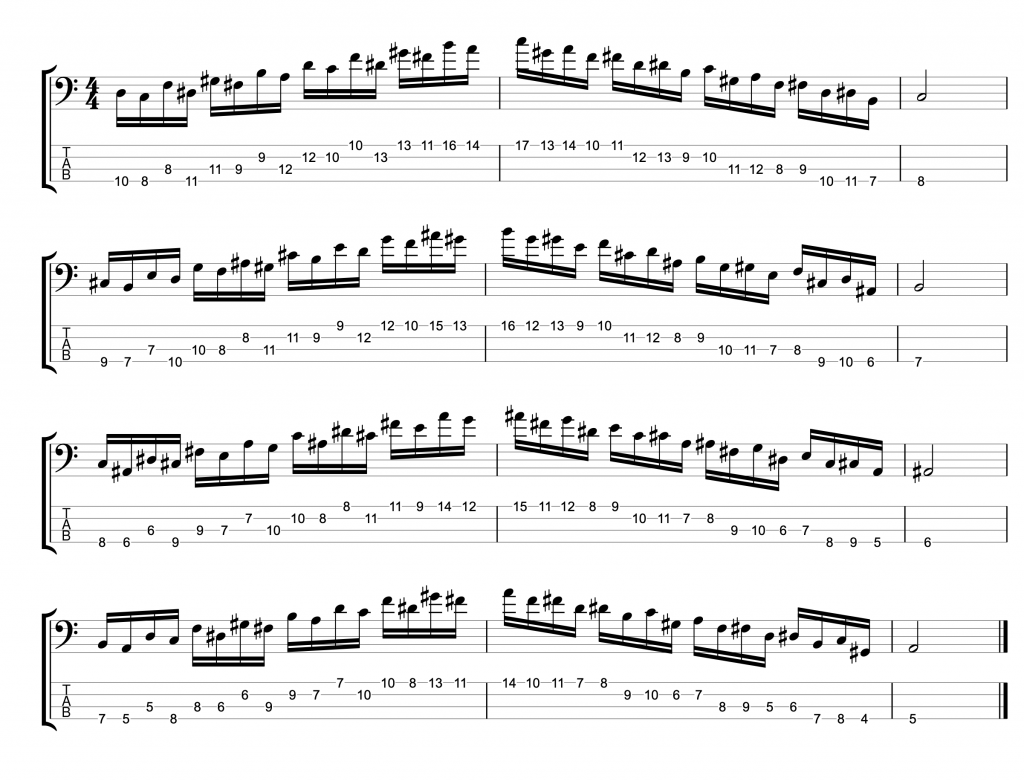
But what if you want to go beyond bebop scales and play more than one chromatic passing note in a line? I’ve given one example in the video of playing a chromatic line that goes from 3rd down to 7th chromatically.
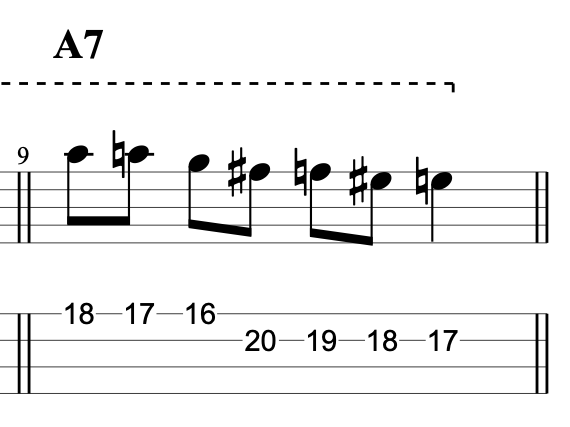
It’s essentially just a sequence from the chromatic scale. But it works as a jazz line because I’ve planned where the chord tones land. The 3rd lands on beat one, the 9th on beat two. The 9th is a chord extension, but it can be treated as a chord tone for the purposes of making jazz lines. Then the root note is on beat three and the 7th on beat four. When you listen to it played against an A7 chord, you can hear the sound of the chord coming from this chromatic line.