How to Make a Major Scale Sound Like Jazz – Bass Practice Diary – 17th November 2020
If you study harmony, you begin to realise just how important the major scale is. Diatonic harmony in its entirety realties to the intervalic relationships of the major scale (also sometimes called the diatonic scale). So, it’s hardly surprising that a major scale is a popular choice for improvisation as well. But, how do you make a major scale sound like jazz?
Why use major scales in jazz improvisation?
I think that a lot of musicians learn to analyse diatonic chord progressions in jazz standards. They know the right key to play at every point in the progression. Each key is defined by the notes of the parent scale, which in the case of major keys, is a major scale. So, you can break a lot of jazz tunes down to playing different major scales at different points in the chord progression. But the problem is, that major scales on their own don’t sound very much like jazz. So, how do you use the major scale to make jazz lines?
I’ve noticed that a lot of people learning to improvise are looking for a scale or scales that will make them sound like jazz. I don’t think it works like that. I think there are a lot of different approaches to improvising in a jazz style. Today, I’m looking at two key concepts. One is approach notes, the other is outside notes. The concept of outside notes is simple to understand. There are seven notes in any key (the notes of the major scale) and there are twelve notes in the octave (the chromatic scale). Outside notes are the five other notes that are not in the major scale. If you want your lines to sound like jazz lines, you need to come up with some creative ways to use them.
A simple and great way to begin to incorporate some outside notes into a major scale, is with the use of chromatic approach notes. A chromatic approach note can be as simple as picking a target note from the parent scale, and playing a semi-tone (one fret) below or above that note before you play it. Of course, not all of these chromatic approach notes will be outside notes. If your target note is the major 7th, and you play a chromatic approach note above that note, you’re playing the root note. But some (most) of your chromatic approach notes will be outside notes. And that’s enough to bring a jazz flavour to your lines.
Play a major scale with chromatic approach notes
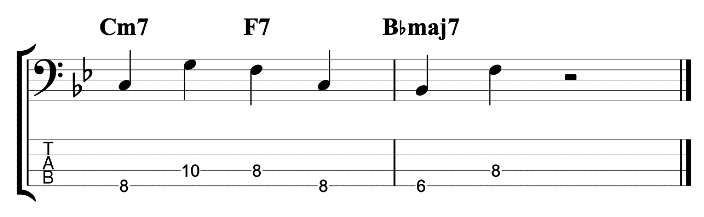
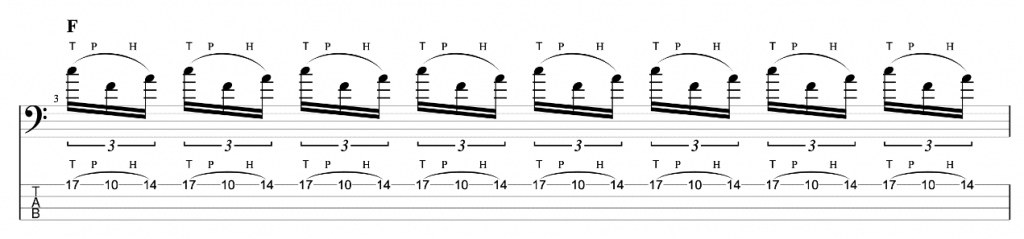
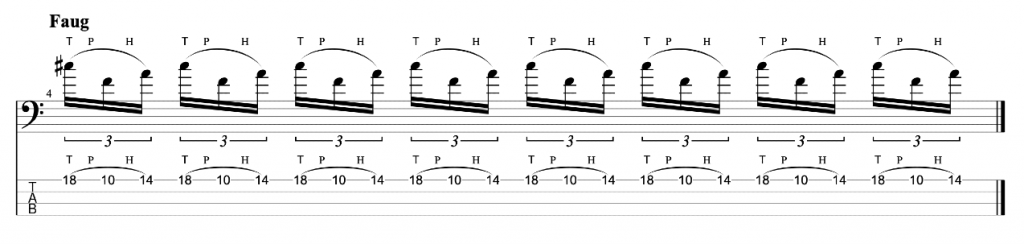
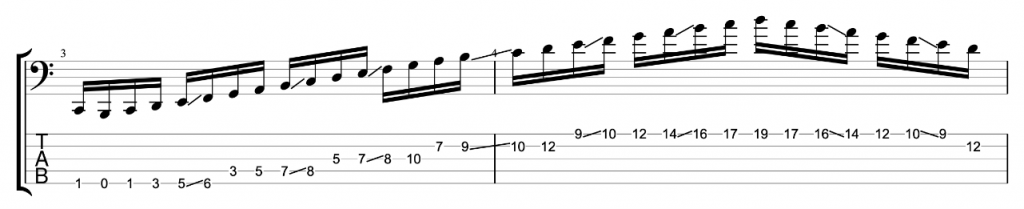
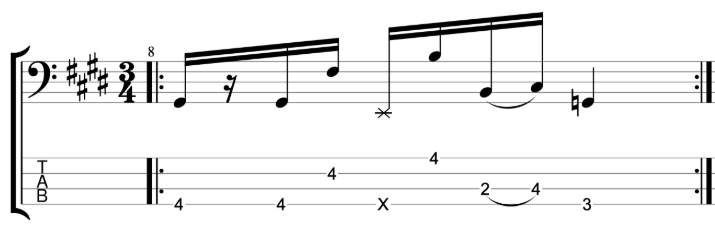
This is an exercise that I featured in the video.

I’m playing a C major scale in ascending thirds (root, 3rd, 2nd, 4th, 3rd, 5th etc). Each third interval is two notes. I’m then adding a chromatic approach note before and below the first, lower note. So, C, E (Root, 3rd) becomes B, C, E, a three note grouping. D, F (2nd, 4th) becomes C#, D, F.
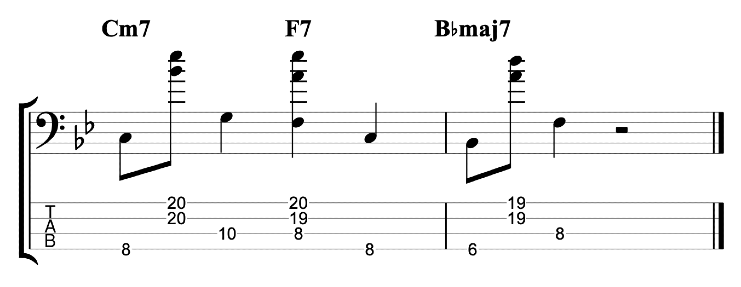
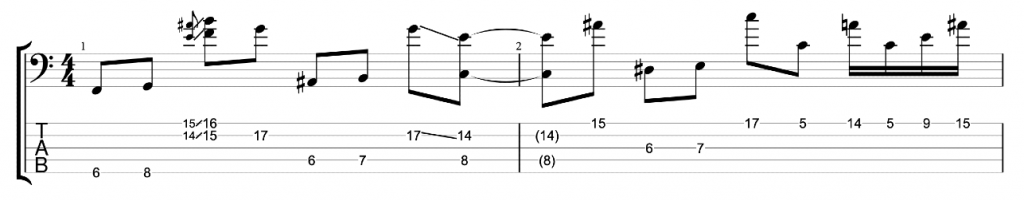
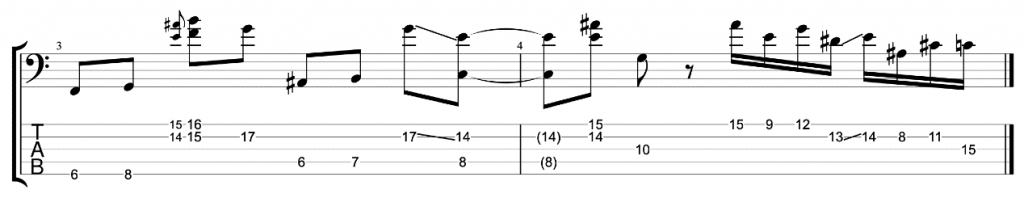
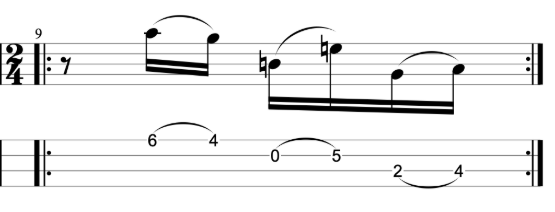
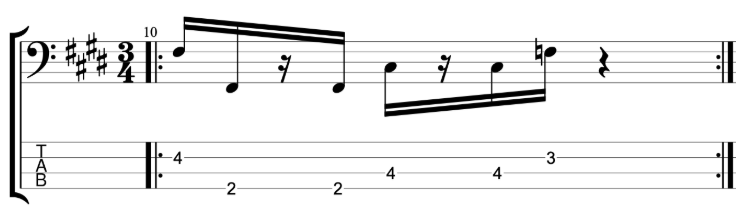
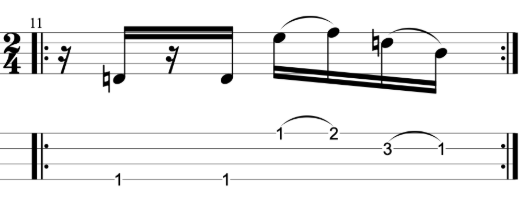
It sounds good, but it sounds like an exercise. I want to make it sound less like an exercise and more like an improvised jazz line. Try mixing up the exercise by varying the chromatic approach notes either above or below the target notes. You can also vary whether you play your thirds ascending or descending. When you play a descending third you can play the approach note before the higher of the two notes.
Here’s an example that I played in the video.