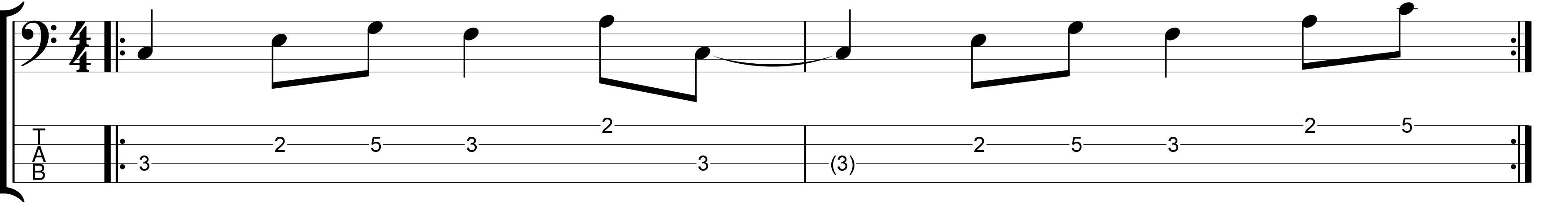
Eighth and Sixteenth Note Bass Grooves
In this video lesson you’ll learn all about sixteenth note bass grooves. How they differ from eighth note grooves and some practical advice for practising them.
What’s the difference between eighth and sixteenth note feels?
I explained in Part 1 of this lesson that when you divide a beat into two, you get an eighth note feel. If you divide each beat and each off-beat into two, so that each beat is divided into four, then you will have a sixteenth note feel.
When you play eighth note grooves, you can place notes either on the beat or off the beat. On Ta or on Ka. When playing sixteenth note grooves you can still place notes on the beat, but there are now three different places where you can place notes off the beat.
There is still a conventional off-beat, as there was with eighth note grooves. This is the point in time exactly equally distant from the beat before and the beat after. However, there are now two other sub-divisions. The first comes between the beat and the off-beat, and the second comes after the off-beat. All four sixteenth note sub-divisions must be equal. None of them is longer or shorter than the others.
Learn to feel all four sixteenth note sub-divisions individually.
In Part 1 I explained that in order to groove in an eighth note feel, you must feel the beats and the off-beats. So if you want to groove while playing a sixteenth note feel, then you must also feel the other two sixteenth note sub-divisions. And, to have great timing you should be able to accurately place a single note on any sixteenth note sub-divisions.
Each of the four sub-divisions has it’s own unique feel when you place a single note on it. Just as the beat has a very distinct feel from the off-beat. So the other two sixteenth note sub-divisions have their own distinct feel.
How do I improve my sixteenth note groove?
First you need four syllables to represent the four sixteenth note sub-divisions, Ta-Ka-Di-Mi. I used Ta-Ka to represent the beat and off-beat in eighth note grooves. For sixteenth note grooves Ta is the beat, Di is now the off-beat and Ka and Mi represent the additional sixteenth note sub-divisions.
As with eighth note grooves, the key to having great timing is the ability to place a single note very accurately onto a sub-division. If fact that is the key to having great timing no matter what the feel or style of music. So begin by trying the exercise demonstrated in the video. Say Ta-Ka-Di-Mi, making sure you say it in time, with every syllable equal in length. Use a metronome or drum beat to help if you need to. Then try playing a single note on each of the four syllables. First Ta, then Ka, then Di, then Mi. This should help you to experience the different feels of the four sub-division.
Once you’ve done that, try playing this sixteenth note example from the video slowly.
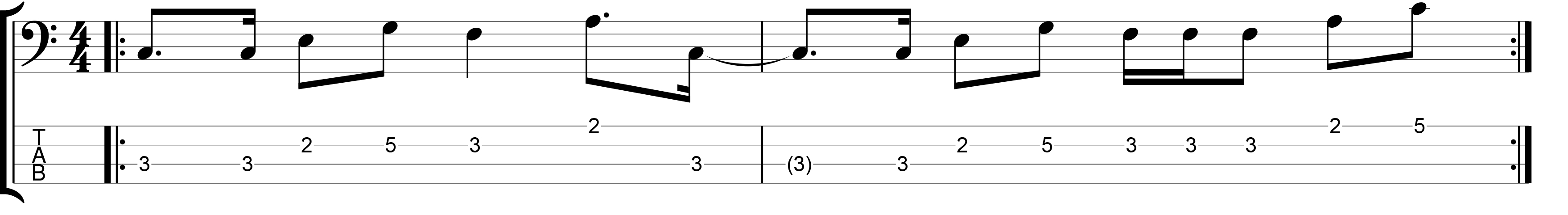
Try reciting Ta-Ka-Di-Mi while you play it, as I’ve demonstrated in the video. Play it as slowly as you need to in order to place all of the notes accurately. Once you can do that, try gradually increasing the tempo. Don’t try playing the example fast until you’ve mastered it slowly.
Why you should always start by practising slowly
A good rule of thumb to remember is this. If you can’t play something in time slowly, your time feel won’t be good when you play faster. I’ve often heard students say that it’s harder to play something slow than fast. It can often feel that way. The reason is that playing something slowly makes all of the little errors of timing very obvious. They’re not so obvious when you play fast. However, if you want to improve your groove, you need to get rid of those little timing errors. Those notes that are placed slightly before or after the sub-division they were meant to be on. And that involves playing very accurately slowly, and then gradually speeding up while maintaining the same levels of accuracy. That’s how you improve your bass groove!
All of the examples in this series of videos come from my book Electric Bass – Improve Your Groove: The Essential Guide to Mastering Time and Feel on Bass Guitar.

Click on the link to find the book. https://geni.us/bassgroove.
The book contains over 140 audio examples featuring eighth and sixteenth note grooves in a variety of styles including rock, blues, jazz and latin. It also features sections on syncopation, shuffle feels, triplets and swing. It has practical advice for grooving with drums and sharing a collective time feel in a group. And it features five pieces with play along backing tracks to help you put these ideas into practice.
Happy practising!